The Invisible Web: Demystifying Computer Networks and Their Power
Imagine a digital highway where data zips between devices at lightning speed—this is the magic of computer networks. From your home Wi-Fi to the sprawling infrastructure of global corporations, networks are the unsung heroes of our connected world. Let’s unravel how they work, why they matter, and what the future holds.
What Is a Network?
A network is a team of devices—computers, printers, smartphones—linked together to share data. Whether connected by cables, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth, these devices “talk” to each other, creating a web of communication.
Types of Networks: From Your Living Room to the Globe
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- Connects devices in a single space: homes, offices, or schools.
- Example: Your home Wi-Fi network.
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
- Links networks across cities or countries.
- The internet is the ultimate WAN.
- PAN (Personal Area Network)
- Tiny networks like your phone syncing with a smartwatch via Bluetooth.
- WLAN (Wireless LAN)
- A cable-free LAN, powered by Wi-Fi.
Network Components: The Building Blocks
- Modem: Bridges your network to the internet.
- Router: Directs traffic between devices and the web.
- Switch: Connects wired devices (like office PCs).
- Network Interface Card (NIC): Lets devices join the network.
- Cables: Ethernet or fiber optics for speedy, stable links.
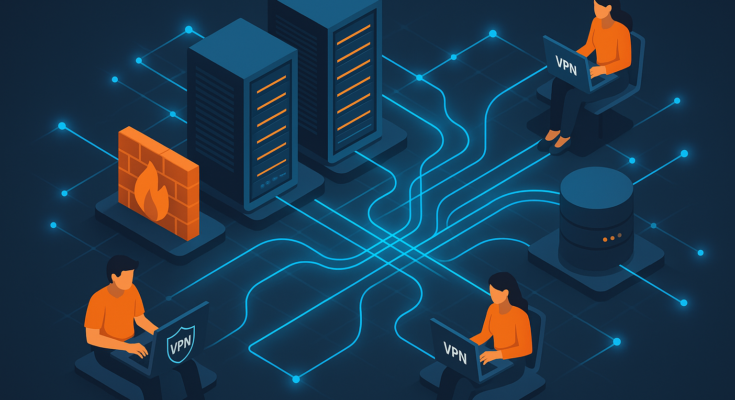
Security: Guarding the Digital Gates
Networks can be open (risky) or password-protected (secure). Public Wi-Fi? Beware! Use a VPN to encrypt your data and stay invisible to hackers.
Why Networks Rule
- Share files or printers effortlessly.
- Power multiplayer gaming and video calls.
- Fuel the internet and smart home gadgets.
The Future of Networks: Faster, Smarter, Safer
- Speed: 5G and Wi-Fi 7 are rewriting the rules of connectivity.
- AI Integration: Networks that self-optimize and predict issues.
- Stronger Encryption: Keeping data leaks at bay.
Enterprise Networks: The Backbone of Businesses
Companies rely on complex networks to connect employees, servers, and global offices. Think of it as a digital nervous system linking:
- Devices: Laptops, printers, smartphones.
- Servers: Hosting emails, databases, and apps.
- Security Tools: Firewalls, antivirus software, VPNs.
Key Components in Corporate Networks
- Servers: The brains storing critical data.
- Firewalls: Digital bouncers blocking cyber threats.
- Switches & Routers: Traffic controllers for seamless internal and external links.
- Fiber Optics: Superfast cables for data highways.
Types of Corporate Networks
- LAN: Links devices in one office.
- WAN: Connects global branches.
- Intranet: A private hub for internal docs and tools.
- VPN: Secure tunnels for remote workers.
Security in Corporate Networks
With sensitive data at stake, companies deploy:
- Firewalls and antivirus software.
- Access controls to limit who sees what.
- 24/7 monitoring and automated backups.
Who Manages These Networks?
IT teams or network administrators handle:
- Designing and troubleshooting networks.
- Upgrading hardware and software.
- Training employees on cybersecurity.
Why Networks Are Vital for Businesses
- Streamline teamwork and file sharing.
- Run critical systems like payroll and CRM.
- Support remote work (a post-pandemic must!).
Case Study: A Three-Story Office Network
- Each floor has its own LAN.
- A central switch ties them together.
- Routers link to the internet.
- Servers and firewalls guard data.
- Employees print, share files, and collaborate securely—no matter their location.